Sales Territory Mapping: Strategy, Use Cases, and Software
Sales territory mapping converts customer data into a visual plan, ensuring balanced coverage and focus on key markets. In this guide, you’ll learn why it matters, how to build your map, and which tools to use.
Create Your Sales Territory Map
Use the interactive widget below to outline your U.S. sales territories. Click states to group them into regions, name each region, and export your map as a PNG.
Want to embed this map on your website?
- Try the online USA Map Editor
- Or install the US Map Plugin for WordPress/HTML sites
What is Sales Territory Mapping?
Sales territory mapping (often part of territory planning or sales coverage mapping) is the process of organizing a company’s sales areas so that each geographic region or customer segment is assigned to a specific salesperson or team. In other words, a “sales territory” is the customer group or geographic area a salesperson is responsible for, and mapping involves defining the boundaries of those territories and the associated sales targets. By visualizing territories on a map, sales leaders can clearly see who covers which areas and ensure balanced coverage. When done properly, territory mapping helps reps target the right customers and meet revenue goals. In short, effective sales territory mapping turns raw sales data into a visual plan that guides your reps to the most promising markets.
Why It Matters and Common Use Cases
Effective territory mapping ensures that no customer or region is neglected and that sales teams work efficiently. Key benefits and use cases include:
- Balanced Workloads: Properly aligned territories give each rep a manageable workload. Balanced territories boost motivation and performance by avoiding over- or under-servicing. When reps have evenly distributed accounts, companies see higher motivation, lower turnover, and ultimately more sales.
- Increased Sales Productivity: Studies show that data-driven territory design directly improves results. For example, optimizing territory alignment has been linked to a 7–14% increase in sales goal attainment and up to 30% higher sales performance in some cases. This happens because reps spend less time with poorly allocated leads and more time on high-potential customers.
- Targeted Market Coverage: Territory maps highlight geographic or account gaps. For instance, visualization can reveal which areas are under-served. Managers can then reassign zip codes or merge territories to capture hidden opportunities. Modern mapping tools even allow segmentation by industry or customer type within the same region, so multiple reps can work in one area without overlap.
- Data-Driven Decisions: With interactive maps, sales data comes alive. Managers can color-code regions by revenue or add heatmaps, making it easy to spot trends (e.g. hot markets vs. cold zones) and adjust strategy. This data visualization uncovers insights that spreadsheets alone might miss.
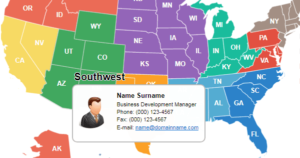
- Use Case Example – Sales Rep Locator: Many companies publish a “sales rep locator” map on their website. By combining states or areas into regions and linking each to a rep’s contact info, customers can easily find their local rep. This is a practical example of territory mapping in action, improving customer experience by showing who covers each region.
By addressing these use cases—balancing territories, focusing on priority markets, and visualizing coverage—sales territory mapping plays a critical role in boosting efficiency and customer reach.
How to Build an Effective Sales Territory Map (Step-by-Step)
Creating a high-impact territory map is a structured process. These steps, based on best practices, will guide you:
- Define Objectives. Start by establishing clear goals: sales quotas, revenue targets, or growth metrics. Align territory planning with your overall business objectives (e.g., % growth in a region or new account targets). Knowing what you aim to achieve (market share vs. account growth) ensures the territory plan supports your strategy.
- Gather Data. Compile relevant data, such as customer locations, historical sales, leads, and demographic or market potential. Accurate CRM or spreadsheet data provides the basis for mapping. Clean, up-to-date information on customers or prospects will make the mapping effort more effective.
- Segment the Market. Decide on how to divide your market into territories. Common factors include geography (states, zip codes), industry/vertical, company size, or product lines. For example, you might create one territory for healthcare clients and another for finance. Smart segmentation (e.g. by sales potential or account type) makes sure every part of your market is addressed.
- Assign Territories to Reps. Allocate the defined territories to your sales reps. Match regions with reps’ expertise and workload. As Salesforce advises, consider each rep’s skills and experience (product knowledge, industry focus) to assign the right territory. Use sales managers’ insights to balance territories—no single rep should have vastly more accounts or travel than others.
- Use Mapping Tools to Draw Boundaries. If possible, use sales mapping software or mapping platforms to draw territory lines on a map. These tools enable you to paint or outline regions (by zip codes or shapes) and automatically calculate totals (accounts, revenue, etc.) per territory. Modern mapping tools can even import your data and balance territories dynamically: for example, they can reassign accounts so each rep’s territory has equal sales potential. This saves hours of manual work.
- Review and Refine. After the initial map is drafted, review it with the team and adjust as needed. Use scenario analysis (merge, split, or shift territories) to test different alignments. As RingCentral suggests, make adjustments based on performance data and rep feedback. Sales territory mapping is not a one-time task; revisit and update your map whenever market or team changes occur.
By following these steps—defining goals, using data-driven segmentation, assigning reps carefully, and leveraging mapping software—you can build an effective sales territory map that maximizes coverage and performance.
Common Segmentation Strategies
Organizations commonly segment territories by logical criteria to match their sales strategy. Effective territory planning often uses one or more of the following:
- Geographic Territories: Divide regions by physical boundaries (e.g. states, counties, ZIP codes). This is the most common approach, ensuring reps focus on customers in nearby locations.
- Product-based Territories: Assign territories based on product lines or service categories. For example, a tech company might have one team selling software products and another selling hardware, each with its own geographic coverage.
- Customer or Account Territories: Segment based on customer type or size. A company might create separate territories for enterprise clients versus small businesses, so reps can tailor their approach to each segment.
- Industry/Vertical Territories: Group customers by industry sector. For instance, one territory covers healthcare clients and another covers financial services. Vertical territories allow reps to develop specialized expertise.
- Sales Channel Territories: Divide by sales channel or distribution type. Companies might separate direct sales teams from reseller or channel partner territories. This is useful if different channels require different coverage strategies.
These strategies (often used in combination) help align territories with business priorities. For example, a company might use geographic segmentation by default but carve out special territories for a new product line or a key customer vertical.
The best approach depends on your market and goals, but recognizing these common types of territory segmentation is a crucial part of territory planning.
Sales Territory Mapping Software: Overview of the Market
Several software solutions can assist with territory mapping, each offering unique features for sales managers:
| Software | Key Features | Website |
|---|---|---|
| Maptive | Draw & optimize territories, heat maps, demographics | https://www.maptive.com |
| Badger Maps | Territory drawing, CRM import, mobile app | https://www.badgermapping.com |
| SPOTIO | ZIP-code/hand-drawn boundaries, pipeline tracking | https://www.spotio.com |
| Mapline | Excel import, custom boundaries, heat maps | https://www.mapline.com |
| eSpatial | Territory creation, analytics dashboards | https://www.espatial.com |
| Geopointe | Salesforce mapping, account assignment | https://www.geopointe.com |
| Maptitude | GIS-grade mapping, demographic data | https://www.caliper.com/maptitude |
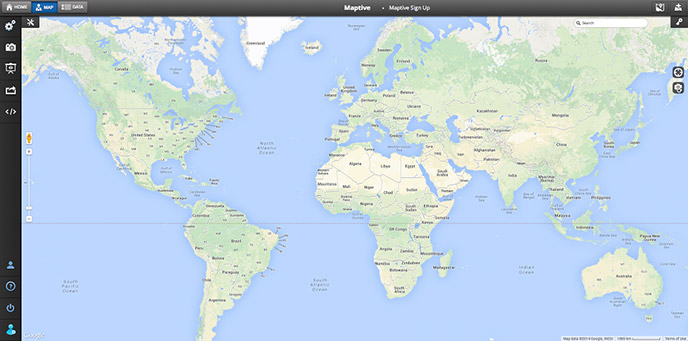
- Maptive: A cloud-based mapping platform that turns spreadsheets into custom Google Maps. Maptive lets you draw sales territories on a map, create heat maps, and view demographic data. It’s popular for transforming raw sales data into interactive territory and density maps quickly.
- SPOTIO: A field-sales mapping tool designed for outdoor sales teams. SPOTIO helps create territories by ZIP code, city, or hand-drawn boundaries. It includes features like pipeline visualization and performance tracking. Spotio claims to boost sales productivity (reportedly up to a 23% increase in sales efficiency). It also offers route planning and territory analytics for mobile sales reps.
- Mapline: A web-based mapping and data visualization tool. Mapline can import data from Excel or other sources, then plot points and color-code territories. Key features include adding boundaries, generating heat maps, and assigning customers to territories automatically. It’s used for market planning, account mapping, and logistics optimization, and is noted for its ease of turning spreadsheet data into maps.
- eSpatial: An all-in-one mapping solution for territory management and route planning. eSpatial provides data visualization, territory creation, and CRM integration tools. Users can draw and optimize sales territories, then plan multi-stop routes for field teams. Its platform emphasizes an intuitive interface for analyzing territory performance and making data-driven adjustments.
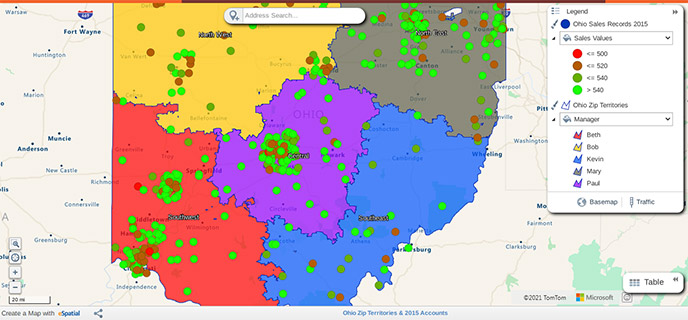
- Geopointe: A Salesforce AppExchange app that brings mapping into Salesforce CRM. Geopointe lets you visualize accounts and leads on a map directly in Salesforce. It supports territory building by standard boundaries and can automatically assign or reassign accounts. Features include real-time field tracking and integrated route planning. While built for Salesforce users, Geopointe exemplifies how mapping software can tie CRM data to geographic territory design.
- Maptitude: A GIS software package by Caliper, aimed at analysts. Maptitude provides detailed mapping and demographic data to support territory analysis. You can import your own data (or use included street/base maps) and draw custom territories. It’s often used for sophisticated market analysis – for example, identifying “hidden” sales opportunities or answering geographic questions that traditional reports cannot.
Each of these tools offers interactive sales map visualization and territory management features, such as coloring regions, analyzing sales performance by area, and reporting on territory balance. Choosing among them depends on factors like your data sources, budget, and required features (for instance, do you need CRM integration, or just a standalone mapping interface?). The important point is that sales territory mapping software combines geographic mapping with sales data insights, enabling much more informed territory planning than manual methods.
Where Website Maps Fit In
While dedicated mapping software helps plan and analyze territories, an interactive website map is a simpler way to present territory information on your public site. Fla-shop’s tools are designed for this purpose: to display territory assignments on a website rather than manage them. For example, Fla-shop’s USA map plugin (for WordPress or any HTML site) can be customized so that states or regions are color-coded by sales rep. You can add clickable state regions with pop-up balloons showing each rep’s name and contact info. This is great for a “Sales Rep Locator” feature – e.g., combining states into a West region for one rep and a Southeast region for another.
The Fla-shop Map Editor also allows you to draw custom territories and embed the map on your site without coding. In practice, you would use the editor to fill colors or add content (such as addresses or performance data) and then copy an embed code or install the WordPress plugin. The result is an interactive map on your company website, letting visitors click on a state/region and see the assigned rep or relevant data.
These website maps are meant for visualization and communication. They let you display who covers which region (enhancing customer usability) and do not replace full-featured territory management software. In other words, use Fla-shop maps when you need an attractive, interactive map on your website (for example, to show customers their local rep), while using more powerful mapping tools behind the scenes for detailed territory planning and analytics.
FAQs
What is a sales territory map used for?
A sales territory map shows which areas or accounts each salesperson covers. It helps sales teams organize territories by geography or customer type and assign reps accordingly. In practice, a territory map guides reps on where to focus: it can highlight high-potential regions, prevent overlap, and clarify coverage responsibilities.
Why is sales territory mapping important?
Mapping territories matters because it aligns sales efforts with strategy and data. Balanced territory design ensures equal workload, which boosts rep productivity and morale. Studies show that data-driven territory alignment can significantly lift sales outcomes (for example, up to ~7–30% improvements in performance). In contrast, unbalanced or haphazard territory plans lead to inefficiency and missed opportunities. Mapping also makes it easy to spot under-served areas or emerging market trends, so teams can quickly adjust strategies.
What factors should I consider when designing territories?
You should consider criteria like geography (state, region, ZIP code), customer demographics, industry verticals, and account size or potential. For example, Segmenting by region and company size ensures every area and client type is covered. Other factors include rep expertise (sales experience, product knowledge) and territory workload (total number of customers or revenue target). A good plan often balances geographical proximity with customer value so that no single territory is too large or too “empty”.
What features should sales territory mapping software have?
Look for tools that link your sales data to interactive maps. Key features include the ability to import data (like account locations), draw or modify territory boundaries, and instantly calculate metrics (total accounts, sales potential, etc.) for each territory. Advanced software can automatically balance territories by key attributes and let you model “what-if” scenarios. In other words, the software should combine geographic visualization with analytics, so you can design equitable territories based on customer data. Usability (easy map drawing) and good reporting (performance by territory) are also important features.
How do embedded website maps differ from territory mapping software?
Website maps (like Fla-shop’s Embedded Maps) are for displaying territory information publicly. They show on a website which rep covers each region, usually with interactive pop-ups (e.g., rep contact info by state). By contrast, territory mapping software is used internally for planning. Mapping software includes data integration, territory optimization algorithms, and reporting. In short, an embedded web map visualizes the final assignments for customers or staff, while a mapping software tool helps create and analyze those territories behind the scenes.
Is sales territory mapping only for large companies?
Not at all. Any business that has a sales team and distinct market areas can benefit. Even small businesses gain efficiency by defining territories. It helps focus efforts on the most promising regions or customer segments. As RingCentral notes, a territory plan lets you target specific industries or regions rather than “spray and pray”. It also ensures reps spend their time selling to the right customers, which can significantly improve results. In short, well-designed territories help companies of all sizes set realistic goals, track progress, and close more deals.
Try the Map Tool
Ready to visualize your own sales territories? Fla-shop offers an interactive demo and tools you can try right away. Use the United States Map Editor on Fla-shop’s site to paint territories and add rep information — it’s free to sign up and requires no coding. Or download the Fla-shop US Interactive Map plugin for WordPress/HTML and create a custom territory map on your site. These tools let you combine states into regions and embed the resulting map on your website in just a few clicks. Give it a try and see how easy it is to display your sales coverage in an interactive map!